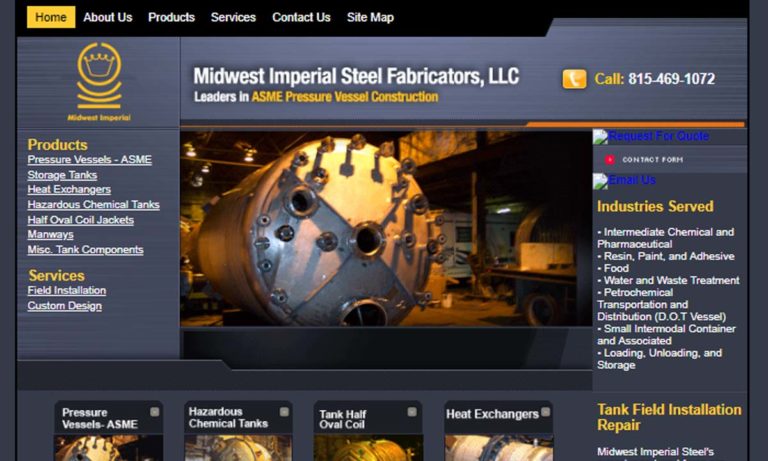
Pressure vessels are use to contain fluids, vapors or gases for the purposes of storage, mixing or transportation. Read More…
If you are looking for innovative pressure vessels, you’ve come to the right place! We actively manage your project every step of the way. We keep you informed of what we are doing to ensure we keep up to your standards and delivery times.
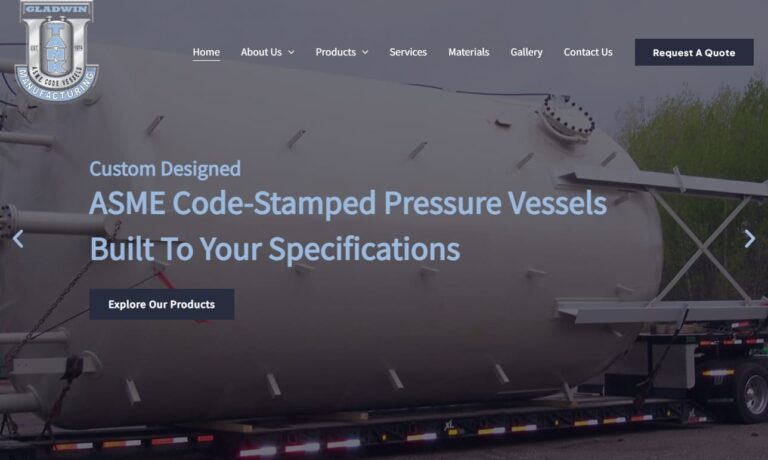
Gladwin Tank Manufacturing builds custom ASME pressure vessels. We work with stainless, carbon, duplex and the nickel alloys and offer custom rolling, plasma, and water jet cutting. Paired with our expertise in multiple welding procedures, we’re capable of handling every project, large and small. Contact us for your custom build requirements. We are more than just pressure vessels, we...
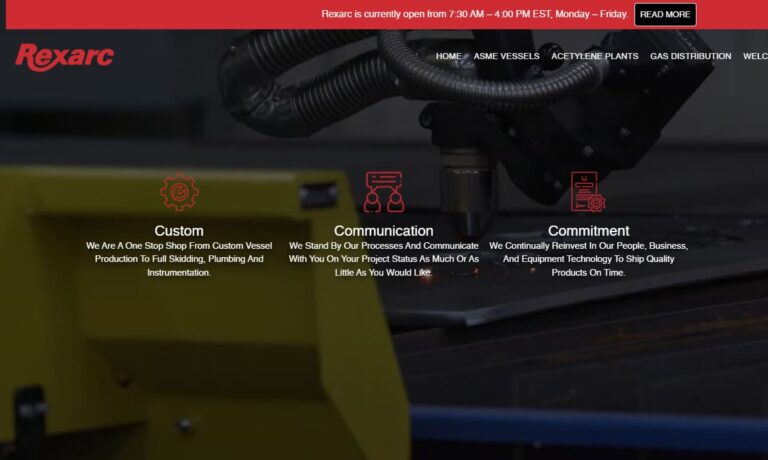
Rexarc’s focus is on the fabrication of custom stainless and carbon steel pressure vessels. We welcome applications with pressures between 500 and 5,000 psi. After nearly 100-years of being in business, Rexarc has the knowledge, attitude, equipment, and processes to support your needs in vessel production and value add services of piping, instrumentation, paint, and other controls...
Midwest Tank Company has provided quality tanks to small and large corporations and contractors since 1972. Our reputation is built on exceptional services and customer satisfaction! Our fabrication techniques have been developed through years of tank specialization, combined with personnel who are experienced in all phases of our operation.

Vector Systems, Inc. is a leading provider of Process Control Equipment, specializing in comprehensive solutions for the Chemical, Power Generation, and other Industrial sectors. With a strategic focus on innovation and reliability, Vector Systems has become a trusted partner, offering a wide range of products and services tailored to the unique needs of demanding industries.

More ASME Tank Manufacturers
ASME Pressure Vessels: Manufacturing Standards, Applications, and Industry Insights
The ASME code of vessel manufacturing standards is considered the gold standard in the design, fabrication, and inspection of pressure vessels and storage tanks worldwide. Industries across the globe rely on the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) to ensure the highest levels of safety, quality, and performance in their process equipment.
What are ASME Pressure Vessels?
ASME pressure vessels are specialized containers designed to hold liquids or gases at a pressure substantially higher than ambient atmospheric pressure. These vessels are engineered, constructed, tested, and certified in accordance with the strict guidelines set by the ASME BPVC. The code covers critical factors such as material selection, design calculations, welding procedures, nondestructive examination (NDE), hydrostatic testing, and ongoing inspection and maintenance requirements.
Why Choose ASME-Certified Tanks? Key Benefits for Your Operation
Opting for ASME-certified tanks delivers a host of advantages for businesses in sectors such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, petrochemicals, oil and gas, plastics, water treatment, power generation, and beyond. Key benefits include:
- Guaranteed Safety and Reliability: ASME vessels are designed to withstand rigorous operating conditions, minimizing the risk of catastrophic failure, leaks, explosions, or hazardous releases.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions require ASME certification for pressure vessels used in commercial and industrial processes, simplifying permitting and inspections.
- Longevity and Durability: High-grade materials, advanced fabrication techniques, and strict inspection protocols ensure a longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
- Insurance and Liability Protection: Using ASME-certified pressure vessels can lower insurance premiums and reduce legal liability in the event of an incident.
- Global Acceptance: The ASME stamp is recognized internationally, enabling equipment to be shipped, installed, and operated across borders with confidence.
Primary Applications of ASME-Standard Pressure Vessels
ASME tanks are integral to a diverse range of industrial applications, including but not limited to:
- Chemical Processing: Storing and mixing of hazardous chemicals, solvents, and process fluids under controlled pressure and temperature conditions.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Sterile storage and pressure-reactor vessels for batch processing, fermentation, and blending of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Food and Beverage Production: Sanitary tanks for the storage, fermentation, pasteurization, and carbonation of beverages and food products.
- Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical Industries: Crude oil separation, hydrocarbon storage, fuel gas conditioning, and process containment.
- Power Generation: Steam drums, heat exchangers, and condensate tanks for thermal and nuclear power plants.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Pressurized storage, filtration, and chemical dosing tanks.
- Plastics and Polymers: Reactor vessels for polymerization and chemical synthesis.
- Compressed Air and Gas Storage: Air receivers, gas cylinders, and accumulators for industrial automation and process control.
Want to discover which ASME vessel type fits your process? Explore common ASME pressure vessel types and their specific uses.
Understanding ASME Code Compliance: What Do Engineers Need to Know?
Engineers must strictly adhere to the ASME BPVC when designing and specifying pressure vessels and tanks. Critical factors include:
- Materials Selection: Only code-approved, traceable materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium, nickel alloys, and high-strength thermoplastics are permitted, based on compatibility and process requirements.
- Design Calculations: Engineers calculate minimum wall thickness, maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP), and other essential properties to ensure safe operation.
- Temperature Range and Pressure Level: Vessels are rated for specific temperature and pressure ranges. These requirements affect material choice, weld procedures, and testing methods.
- Fabrication Techniques: ASME code allows for certified welding, forging, brazing, and other approved joining methods. Each weld is subject to inspection and documentation.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Ongoing inspections are mandated during fabrication and throughout the vessel’s service life, including visual inspections, radiography, ultrasonic testing, and hydrostatic pressure testing.
Curious about ASME vessel inspection schedules or how to maintain compliance? Learn more about ASME inspection and maintenance best practices.
How are ASME Pressure Vessels Constructed? Key Manufacturing Processes
The construction of an ASME-certified vessel involves several critical steps, each designed to ensure structural integrity, safety, and performance:
- Forging: Shaping metal components under high pressure and temperature to achieve desired strength and grain structure.
- Welding: Joining metal plates, shells, and heads using certified welding procedures (SMAW, GTAW, MIG, etc.) to create leak-proof, pressure-resistant seams.
- Brazing: Bonding metal parts with a filler at high temperatures, often used for specialized assemblies or non-ferrous materials.
After fabrication, vessels undergo rigorous nondestructive examination (NDE) and hydrostatic pressure tests to verify integrity before receiving the ASME stamp.
Customization Options: Tailoring ASME Tanks to Your Application
Every industrial process is unique, and ASME pressure vessels can be custom-engineered to meet specific operational requirements. Common customization options include:
- Removable or Fixed Lids: For easy cleaning, inspection, or secure sealing of contents.
- Tank Supports and Stands: Saddles, legs, or skirts for stable installation, whether horizontally or vertically oriented.
- Access Ladders and Stairways: Safe personnel access for large storage tanks or elevated installations.
- Sight Glass Windows: Real-time monitoring of liquid levels or process conditions inside the vessel.
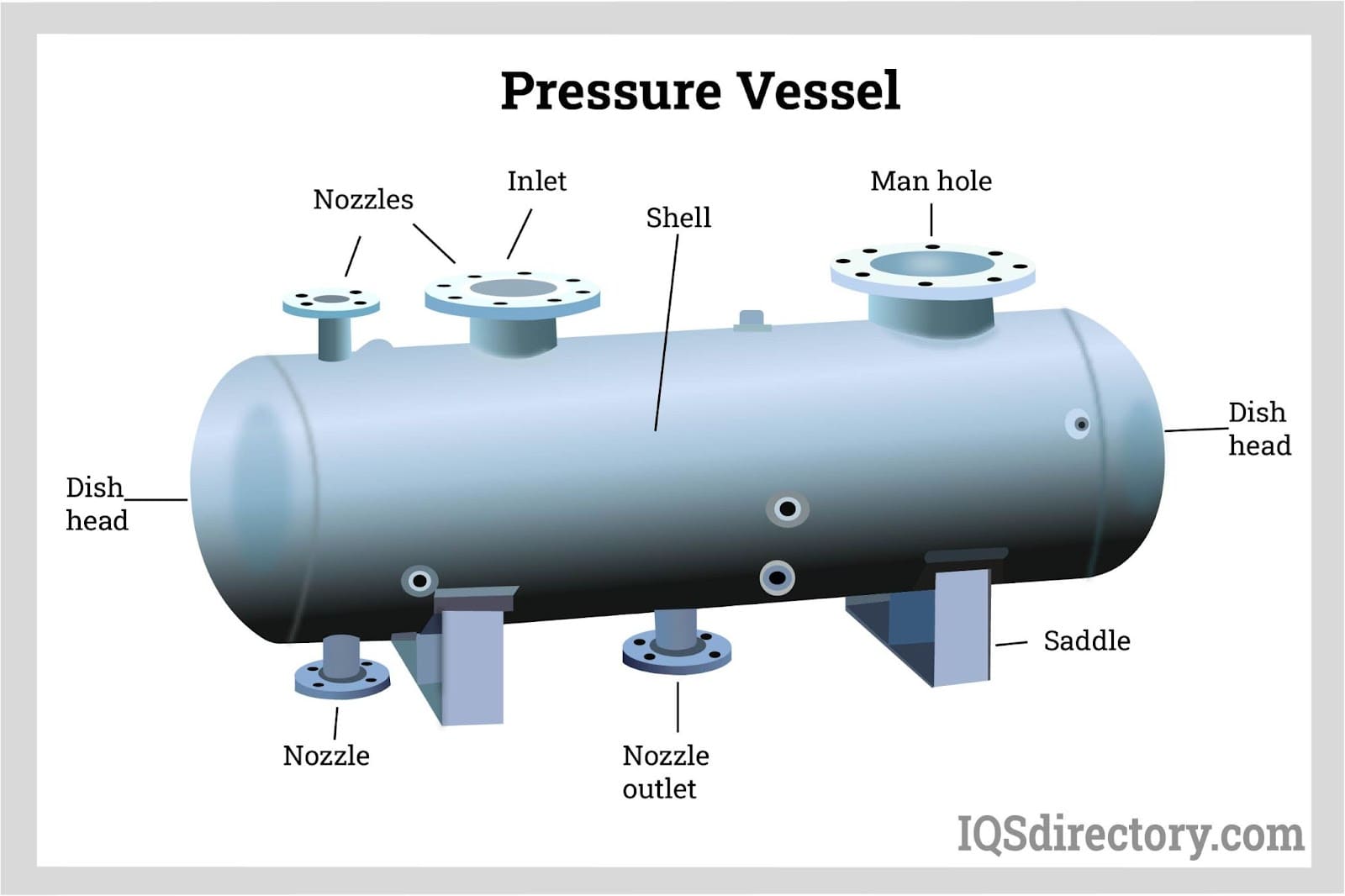
- Process Plumbing Connections: Inlets, outlets, nozzles, manways, and instrumentation ports tailored to your process flow and control needs.
- Heating and Cooling Jackets: For temperature-sensitive applications requiring process heat or chilling.
- Surface Finishes: Sanitary or corrosion-resistant linings and coatings as required by FDA, USDA, or other regulatory bodies.
Not sure which features matter most for your application? Compare ASME tank customization options and decision factors.
Typical Sizes and Installation Configurations for ASME Tanks
ASME pressure vessels are available in a wide range of sizes, measured in gallons or liters according to their capacity. Standard sizes can range from as small as 50 gallons for pilot-scale or laboratory use, to several thousand gallons for large-scale industrial operations. Custom tanks exceeding 100,000 gallons are available for specialized applications such as bulk chemical storage or municipal water treatment.
Installation configurations include:
- Horizontal or Vertical Orientation: Determined by footprint, process flow, and available space.
- Above-Ground or Underground Placement: Chosen based on access, safety, environmental, and regulatory considerations.
- Portable Tanks: Smaller vessels mounted on trucks or trailers for mobile mixing, storage, or emergency response.
Need help sizing a pressure vessel for your project? Read our comprehensive guide to ASME tank sizing and selection.
Material Choices: Which Metals and Polymers Are Used in ASME Vessel Construction?
Material selection is a critical decision in the design of ASME pressure vessels, directly impacting safety, durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Common materials include:
- Stainless Steel: Resistant to corrosion, ideal for sanitary and high-purity applications (e.g., food, pharma, biotech).
- Carbon Steel: Cost-effective and strong, well suited for oil, gas, water, and compressed air applications.
- Nickel Alloys and Titanium: Used for highly corrosive or high-temperature processes (e.g., chemical reactors, specialty gas storage).
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, used in select industries where weight is a concern.
- High-Strength Thermoplastics: For applications requiring chemical resistance or non-metallic vessels.
Wondering which material best fits your process fluid? See our detailed comparison of ASME vessel materials by industry and application.
Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance: Ensuring Long-Term Safety and Compliance
To guarantee ongoing safety and regulatory compliance, ASME pressure vessels must undergo regular inspection, testing, and preventive maintenance. Key steps include:
- Visual Inspections: Checking for surface defects, corrosion, leaks, or weld anomalies during operation and shutdowns.
- Nondestructive Testing (NDT): Ultrasonic, radiographic, magnetic particle, or dye penetrant testing to detect subsurface flaws.
- Hydrostatic Testing: Filling the vessel with water and pressurizing it above normal operating pressure to ensure structural integrity.
- Documentation and Recordkeeping: Maintaining test reports, inspection logs, and repair records for regulatory audits.
- Planned Maintenance: Routine cleaning, valve and gasket replacement, and component upgrades to extend vessel lifespan.
How often should your ASME vessel be inspected? Check industry-recommended inspection intervals and best practices.
Common Types of ASME Pressure Vessels and Their Use Cases
Selecting the right type of ASME pressure vessel is crucial for optimizing process efficiency and safety. Popular vessel types include:
- Storage Tanks: For storing liquids, gases, or bulk chemicals under pressure. Available in vertical, horizontal, and spherical designs.
- Reactors: Vessels designed for chemical reactions, often equipped with agitation and heating/cooling systems.
- Heat Exchangers: Facilitate the transfer of heat between fluids, critical in power plants, refineries, and manufacturing processes.
- Separators: Used to separate oil, water, and gas phases in upstream oil and gas operations.
- Air Receivers: Store compressed air for industrial automation and pneumatic systems.
- Autoclaves: High-pressure, high-temperature vessels used in sterilization and composite manufacturing.
Still unsure which vessel suits your needs? Try our interactive vessel selection tool to match your process with the ideal ASME tank type.
Decision Factors: How to Choose the Right ASME Pressure Vessel Supplier
When researching or purchasing ASME pressure vessels, it’s important to evaluate potential suppliers based on:
- Experience and Certifications: Proven track record, ASME U or UM stamp certification, and relevant ISO or industry credentials.
- Engineering Support: Access to expert design, material selection, and compliance guidance.
- Customization Capabilities: Ability to fabricate vessels to your exact specifications, from size and orientation to accessories and finishes.
- Quality Control Procedures: Documented inspection, testing, and maintenance programs throughout the manufacturing process.
- After-Sales Service: Ongoing technical support, field service, parts availability, and repair/refurbishment options.
- References and Case Studies: Real-world examples of successful ASME tank installations in your industry.
Ready to request a quote? Get started with our ASME pressure vessel supplier checklist and inquiry form.
Industry Trends: Advances in ASME Pressure Vessel Design and Manufacturing
The field of pressure vessel engineering is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in materials science, automation, and digital technology. Current trends include:
- Smart Monitoring: Integration of IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and corrosion inside tanks.
- Advanced Materials: Adoption of duplex stainless steels, composites, and lined vessels for improved performance and corrosion resistance.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Emphasis on sustainable materials, energy-efficient fabrication, and recyclable tank designs.
- Modular and Skid-Mounted Systems: Pre-engineered, factory-assembled tank systems for rapid deployment and reduced onsite construction time.
- Enhanced Safety Protocols: Use of predictive maintenance and automated inspection tools to reduce risk and downtime.
Curious about the future of pressure vessel technology? Explore our in-depth analysis of emerging ASME tank innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions about ASME Pressure Vessels
- What is the difference between ASME and non-ASME pressure vessels? ASME vessels are built and inspected to stringent code requirements, ensuring certification, safety, and compliance, while non-ASME vessels may not meet these standards and could pose operational or legal risks.
- How much do ASME pressure vessels cost? Prices vary based on size, material, design complexity, accessories, and customization. Request a detailed quote from a certified ASME vessel manufacturer.
- What industries require ASME-certified tanks? Sectors like oil and gas, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, water treatment, and power generation often mandate ASME-compliant vessels by law or best practice.
- How do I verify if a pressure vessel is ASME certified? Look for the ASME U or UM stamp on the vessel nameplate, and review the manufacturer’s documentation and certification records.
- Can ASME tanks be retrofitted or modified? Yes, but all modifications must be performed and certified by an ASME-authorized shop, with updated inspection and documentation.
Have more questions? Browse our complete ASME pressure vessel FAQ section.
Conclusion: Why ASME Pressure Vessels are Essential to Industrial Safety and Efficiency
In summary, ASME pressure vessels represent the highest standard of safety, quality, and regulatory compliance in industrial storage and process equipment. Whether you operate in chemical manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, food and beverage processing, oil and gas refining, or water treatment, choosing ASME-certified tanks is a critical decision to safeguard people, assets, and business continuity.
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, work with an experienced, certified ASME tank manufacturer who can provide expert guidance on design, material selection, code compliance, installation, and maintenance. By investing in ASME vessels, you’re not only meeting the needs of today’s industrial processes—you’re preparing your operation for tomorrow’s challenges and opportunities.
Learn more about ASME pressure vessels and request a custom quote today.








 Electric Heaters
Electric Heaters Industrial Dryers
Industrial Dryers Industrial Mixers
Industrial Mixers Industrial Ovens
Industrial Ovens Pressure Vessels
Pressure Vessels Pulverizers
Pulverizers Vibratory Feeders
Vibratory Feeders Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services